Treatment of ingrown toenails
Ingrown toenails (onychocryptosis or Unguis incarnatus) are a common form of nail disease. It is often a painful condition where the nail grows in such a way that it cuts one or both sides of the nail bed.
Bookings for Medaid Clinics (Medaid Ltd.) are provided by FoglaljOrvost.hu.
What is an ingrown toenail?
For any further questions, please contact our expert colleagues at +36-70-268-08-58 or by e-mail at info@medaid.hu.
An ingrown toenail occurs when a piece of the nail penetrates the skin, which can often lead to infection. An ingrown nail can also put pressure on the area where the nail meets the skin without growing into the skin - this is not strictly speaking an ingrown nail, but it can be painful (a corns/ calluses often develop along the side of the nail, which is more a result of this pressure than the nail growing into the skin).
Find out our prices, scroll down or click here!

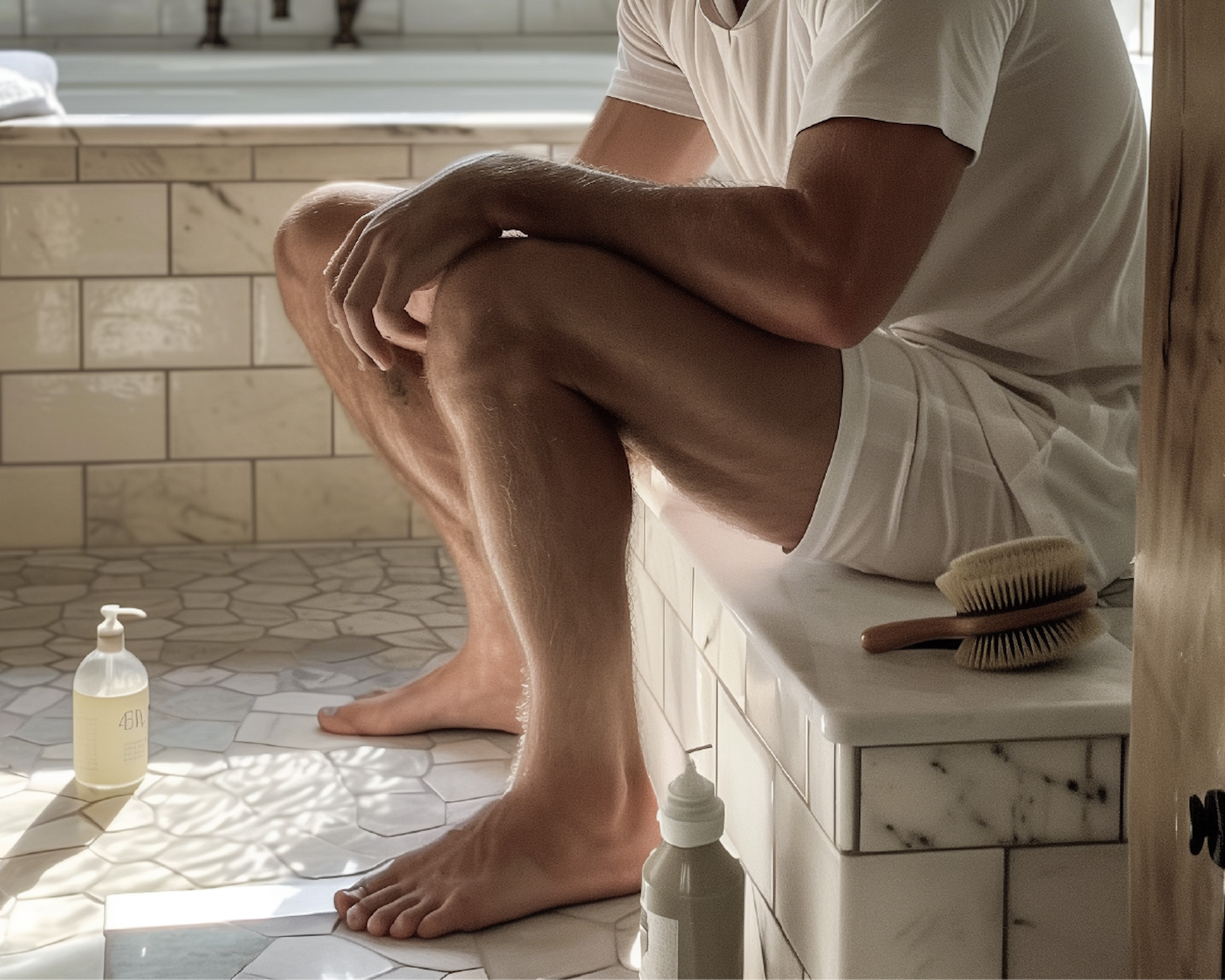
What does an ingrown nail look like?
The side of the nail is often deeply embedded in the skin, making the edge of the nail difficult to see. The severity of the nail growth varies. In some cases the nail is deeply embedded in the skin, only along the edge or edges of the nail. In other cases, the corner of the nail or a small nail spike may pierce the skin like a knife. This can lead to infection and the formation of so-called "flesh" (a scar around the wound). The toe becomes red, inflamed and painful. The area around the nail may swell and sometimes pus may form.
What are the symptoms of ingrown toenails?
The leading symptom of an ingrown toenail is often pain - usually a mild discomfort at first. This can be triggered by pressure from the nail, but can also be caused by the nail actually penetrating the skin along the nail. The pain is increased when wearing shoes or if there is any pressure on the nail. The nail is not necessarily infected, but once the nail grows into the skin, an infection can develop and an ingrown nail can form. A common complication of an ingrown toenail is infection; this can spread and the toe can become red and inflamed (nail biting, paronychia). Signs of infection include redness and swelling of the area around the nail.
Treatment price list
What causes ingrown toenails?
The primary risk factor is the shape of the nail - convex (inward curving) nails are more likely to develop ingrown toenails than flat nails. In some cases, the nail curves downwards for a relatively long distance, at the bend where the nail meets the skin. Much of the nail is almost vertical rather than horizontal. This type of nail most closely resembles a pair of tweezers / pliers - i.e. both sides of the nail are strongly curved. The shape of the nail is most often hereditary (congenital), but can also be affected by traumatic injury and/or shoe pressure. If such a nail is not trimmed properly, it will leave a sharp heel (or worse, a sharp spike) which initially causes symptoms by applying pressure to the skin, but later grows in.
Another common cause of ingrown nails is when the nail is cut too deep on both sides.
Longer shoes are more likely to increase pressure where the skin meets the nail, which increases the risk of ingrown toenails.
Previous damage to the nail can change the shape of the nail, making it more likely to become ingrown.
Toe pressure closer to the ingrown toenail can also be a trigger.
Thicker, pillowy or fuller toes are more likely to develop ingrown toenails. People who often have swollen toes are more prone to developing ingrown toenails.
Treatment of ingrown toenails
An infected, ingrown toenail is often treated with antibiotics, but remember that the cause of the infection (and the ingrown toenail) has not been identified, so there is no point in treating the infection until the cause is found.
Often, our doctors can easily remove the pointed part that has penetrated the skin with relatively little discomfort and local anaesthetic.
Ingrown toenails tend to recur, and the most common reason for this is the shape of the nail itself. In such cases, minor surgery is recommended. It is a relatively simple procedure and can be very successful in providing long-term, permanent relief of symptoms. It is a short, outpatient surgery under simple local anaesthesia: removal of the edges of the ingrown nail along with the inflamed nail beds, and laser treatment of the nail bed to reduce recurrence.

The role of the CO2 laser in the treatment of ingrown toenails
CO2 lasers have been used successfully for years to treat ingrown toenails. The advantages of CO2 lasers over traditional surgical procedures include:
The risk of infection is reduced as the CO2 laser kills bacteria on the surface of the application.
It has a lower recurrence rate than traditional surgery. Recurrence occurs in only 5% of cases within 6 months of surgery!
There is less pain after surgery, so patients can return to their daily activities more quickly than after non-laser surgery.
Bleeding is easier to stop. The laser blocks the small blood vessels in the nail.


Dr. Péter Sándor
Gynecologist, surgeon, proctologist, laser specialist
You are in good hands with us!
Dr Peter is not simply a doctor, but a specialist who approaches every diagnostic task with passion and precision, ensuring that every patient receives the most accurate and detailed assessment.
Csatlakozzon hozzánk és legyen a Medaid csapat tagja!
Várjuk szakorvosok és ápolónők jelentkezését.
Angol nyelvtudás szükséges!
A jelentkezéseket az info@medaid.hu e-mail címre várjuk!